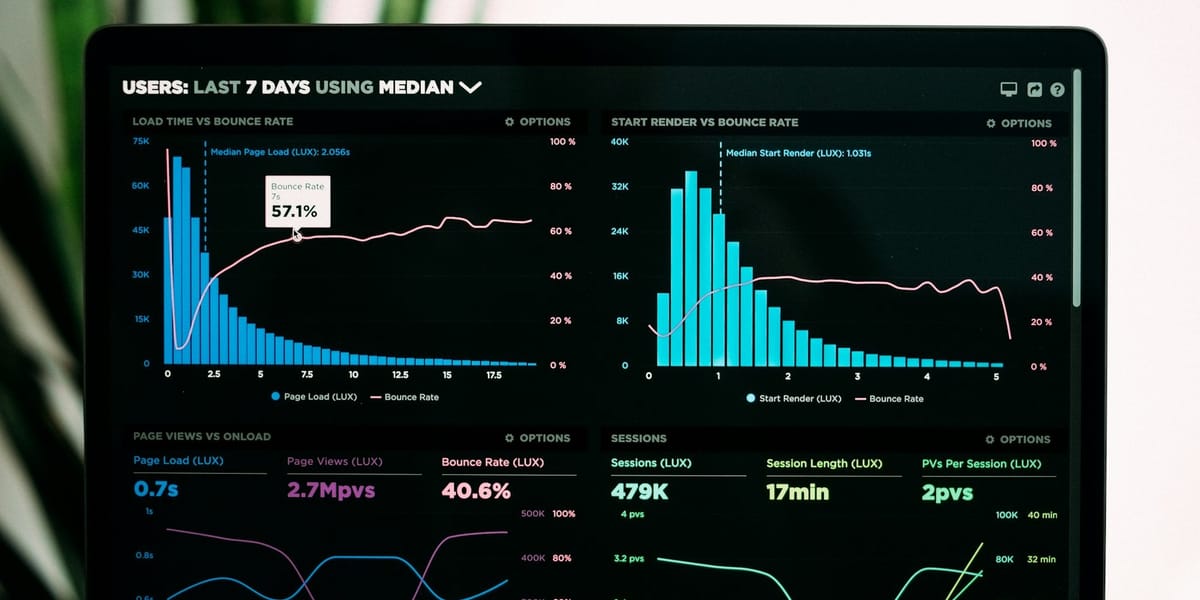
LPG Efficiency, Challenges, and Future Innovations
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) is a widely used fuel in households, industries, and transportation due to its efficiency, versatility, and cleaner-burning properties. It is derived from natural gas processing and crude oil refining, making it an essential part of the global energy market. As the world moves toward sustainable energy solutions, analyzing LPG’s role, benefits, challenges, and future innovations is crucial.
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) is a widely used fuel in households, industries, and transportation due to its efficiency, versatility, and cleaner-burning properties. It is derived from natural gas processing and crude oil refining, making it an essential part of the global energy market. As the world moves toward sustainable energy solutions, analyzing LPG’s role, benefits, challenges, and future innovations is crucial.
Key Aspects of LPG
1. Energy Efficiency and Versatility
LPG has a high calorific value, making it a highly efficient fuel for cooking, heating, industrial processes, and automotive use (Autogas). It burns cleaner than coal and biomass, reducing harmful emissions and improving air quality. Its portability in cylinders and bulk storage tanks makes it accessible even in remote areas.
2. Environmental Impact
LPG is cleaner than traditional fossil fuels, emitting lower CO₂ levels and fewer air pollutants like sulfur and nitrogen oxides. However, it still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. To address this, researchers are developing renewable LPG (rLPG) and bio-LPG, which are produced from sustainable sources such as biogas and organic waste.
3. Economic Significance
The LPG industry plays a crucial role in global energy markets, supporting millions of jobs and energy security. Many governments provide subsidies to encourage LPG adoption, especially in developing countries. However, price fluctuations linked to crude oil markets can impact affordability for consumers.
4. Challenges in the LPG Sector
✅ Price Volatility – LPG prices fluctuate based on global oil and gas markets, making it less stable than some renewable alternatives.
✅ Safety Risks – Being highly flammable, LPG requires proper handling, leak detection, and safety awareness.
✅ Accessibility Issues – In some developing regions, infrastructure limitations make it difficult to distribute LPG effectively.
5. Future Innovations in LPG
🔹 Smart LPG Technology – IoT-enabled gas cylinders with leak detection and auto-refill alerts.
🔹 Renewable LPG (LPG) – Production of sustainable LPG from organic waste.
🔹 LPG in Transportation – Autogas adoption to reduce vehicle emissions and promote cleaner mobility.
Conclusion
LPG remains an essential fuel due to its efficiency, affordability, and cleaner-burning properties. While challenges exist, innovations in smart technology, renewable alternatives, and improved distribution methods will shape its future in the global energy transition.
#LPG #LPG360 #LPGAnalysis #EnergyEfficiency #SustainableFuel #LPGInnovation #CleanEnergy #RenewableLPG #GreenEnergy #LPGMarket #Autogas #LPGSafety #FutureOfEnergy #EcoFriendlyFuel #CarbonReduction #SmartLPG